Optimizing Aqua Farming: Exploring the Critical Role of pH Levels
Aquaculture, a burgeoning industry pivotal for global protein production, demands meticulous attention to environmental factors for the well-being of aquatic life. One of the critical parameters that warrants vigilant management is the pH level of water.
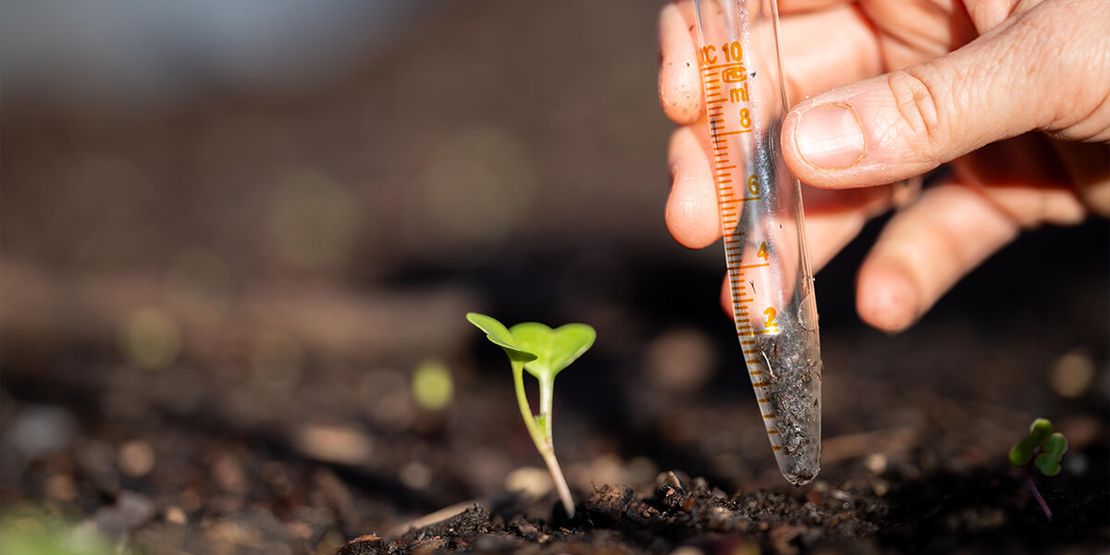
The pH, indicating acidity or basicity, plays a pivotal role in the health and survival of fish and other organisms in aqua farming. Fluctuations in pH levels can lead to detrimental consequences, impacting the growth and prosperity of crops.
Recommended pH Range: Balancing Act for Aquaculture Success
In aquaculture, maintaining the water's pH within a specific range is imperative. The recommended pH range typically falls between 6.5 and 8.5. Straying outside this range can render the water toxic for fish and plants. pH levels can be influenced by various factors, including chemical additions, temperature variations, and the decomposition of organic matter.
Low pH Levels: Nutrient Deprivation and Toxic Threats
When the pH drops below the recommended range, several challenges emerge. One significant issue is the reduction in the availability of essential nutrients. As pH decreases, the solubility of crucial minerals diminishes, impeding the crops' ability to absorb them. This results in stunted growth and diminished yields.
Low pH levels can also trigger the release of toxic metals like aluminum, posing harm to both plants and fish. These metals inflict damage to gills, impairing oxygen absorption and leading to suffocation and mortality. Additionally, low pH conditions foster the proliferation of harmful bacteria and parasites, threatening crops and causing substantial damage.
High pH Levels: Oxygen Deprivation and Stress
Conversely, elevated pH levels bring their own set of challenges. High pH can lead to carbon dioxide buildup in the water, diminishing oxygen availability for plants and fish. This oxygen deprivation induces stress and harm to crops, leading to reduced growth and heightened vulnerability to diseases.
pH Management for Sustainable Success
In conclusion, maintaining the appropriate pH level is paramount for the prosperity and longevity of aqua farming. pH fluctuations can yield significant repercussions, including stunted growth, diminished yields, and increased susceptibility to diseases.
Regular monitoring of pH levels, coupled with timely adjustments, is crucial to ensuring the sustained success and environmental sustainability of the aquaculture industry. By prioritizing pH management, aqua farmers can foster a thriving ecosystem and contribute substantially to global food security.
Recommended for you
Top 10 Best Coffee Shops You Must Try While in Thailand
Tle (Hungry Bear)
Top 10 Most Popular Koh Samui Attractions You Must Visit
Rowan (Guinness Bear)
Optimizing Aquafarming: The Interplay of Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen
Riley Sinclair (Digital Aqua Bear)
Top 10 Best International Health Insurance Companies in Thailand
Rowan (Guinness Bear)