Challenges of Thai Shrimp Farming: Effective Strategies for Success
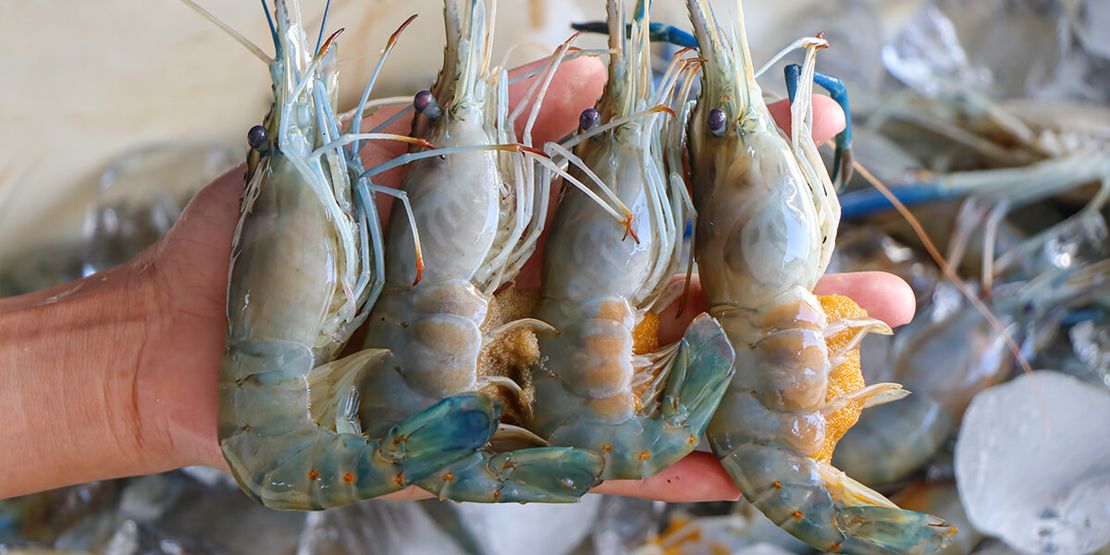
Thai shrimp farming stands as a vital pillar of the country's economy, providing livelihoods for thousands and contributing significantly to its export revenue. However, this lucrative industry is not without its hurdles.
In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the key challenges faced by Thai shrimp farmers and explore strategies to overcome them, ensuring the sustainability and prosperity of this crucial sector.
Disease Outbreaks: Battling the Invisible Foe
Disease outbreaks pose a constant threat to the stability and profitability of Thai shrimp farms. Among the most notorious adversaries is Early Mortality Syndrome (EMS), wreaking havoc on shrimp populations and causing substantial losses. Furthermore, the omnipresent White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) adds to the woes of farmers, compounding their struggles.
To combat these relentless foes, farmers must prioritize stringent biosecurity measures, invest in disease-resistant shrimp varieties, and leverage advancements in disease management technologies. Collaborative efforts between farmers, researchers, and government agencies are also crucial in tackling disease outbreaks effectively and safeguarding the future of Thai shrimp farming.
Environmental Factors: Navigating Nature's Complexities
Thai shrimp farming operates within a delicate ecological balance, where even minor shifts in environmental factors can spell disaster. Fluctuations in water temperature, pH levels, and salinity levels pose significant challenges, directly impacting shrimp health and productivity. Adapting to these environmental dynamics requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing advanced monitoring systems, precision aquaculture technologies, and innovative water management practices.
By harnessing the power of data-driven decision-making and embracing sustainable farming practices, Thai shrimp farmers can navigate nature's complexities and ensure the resilience of their operations in the face of environmental challenges.
Competition from Imported Shrimp: Sustaining Domestic Prosperity
Despite Thailand's status as a global shrimp-exporting powerhouse, fierce competition from imported shrimp presents a formidable obstacle for local farmers. Pressured by lower production costs and varying quality standards in competitor countries, Thai farmers find themselves in a precarious position.
To maintain their competitive edge, farmers must focus on enhancing product quality, streamlining production processes, and differentiating their offerings through certifications such as organic or sustainably sourced labels. Additionally, strategic collaborations with government agencies and industry stakeholders can facilitate market access and promote Thai shrimp's reputation for excellence and reliability.
Labor Costs: Balancing Profitability and Fair Wages
Rising labor costs pose a significant challenge for Thai shrimp farmers, straining operational budgets and profitability margins. With shrimp farming reliant on manual labor for tasks ranging from pond preparation to harvesting, the burden of escalating wages weighs heavily on farmers.
To address this challenge, farmers must explore innovative labor-saving technologies, streamline workflows, and optimize resource allocation. Moreover, fostering a culture of skill development and empowerment can enhance workforce productivity and morale, ensuring a harmonious balance between profitability and fair wages within the industry.
Sustainability Concerns: Pioneering Environmental Stewardship
In an era of heightened environmental consciousness, sustainability emerges as a paramount concern for Thai shrimp farmers. Addressing the industry's reputation for environmental degradation requires a concerted commitment to sustainable farming practices and ecosystem stewardship.
Implementation of Best Management Practices (BMPs), adoption of eco-friendly feed formulations, and integration of mangrove restoration initiatives are pivotal steps toward achieving sustainability goals. Embracing transparency and accountability in supply chains, along with engaging consumers through awareness campaigns, can further enhance the industry's sustainability credentials and foster consumer trust in Thai shrimp products.
Market Volatility: Navigating Turbulent Waters
The volatile nature of the shrimp market presents an ongoing challenge for Thai farmers, with fluctuating prices and demand levels adding uncertainty to business planning and operations. To mitigate the impacts of market volatility, farmers must adopt proactive strategies, including diversification of product offerings, establishment of long-term contractual agreements with buyers, and strategic market intelligence gathering. Embracing digital marketing platforms and exploring emerging market opportunities can also enhance market resilience and reduce dependency on traditional market channels.
Charting a Course for Resilience and Prosperity
In conclusion, the journey of Thai shrimp farming is marked by formidable challenges, yet brims with opportunities for innovation and growth. By embracing a proactive mindset, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering collaborative partnerships, Thai shrimp farmers can navigate the complexities of their industry and emerge stronger and more resilient.
With a steadfast commitment to sustainability, quality, and excellence, the future of Thai shrimp farming shines brightly, promising prosperity for generations to come.
Recommended for you
Rattanakosin Island: An Exciting Round Trip Adventure
Frank, The Bear Traveler
Safeguarding Shrimp Farms: Effective Strategies and Disease Prevention
Riley Sinclair (Digital Aqua Bear)
Living Abroad: How to Adjust to a New Culture and Language?
Lifestyle Bear