Shrimp Feeding: Choosing the Right Feed for Healthy Aquaculture
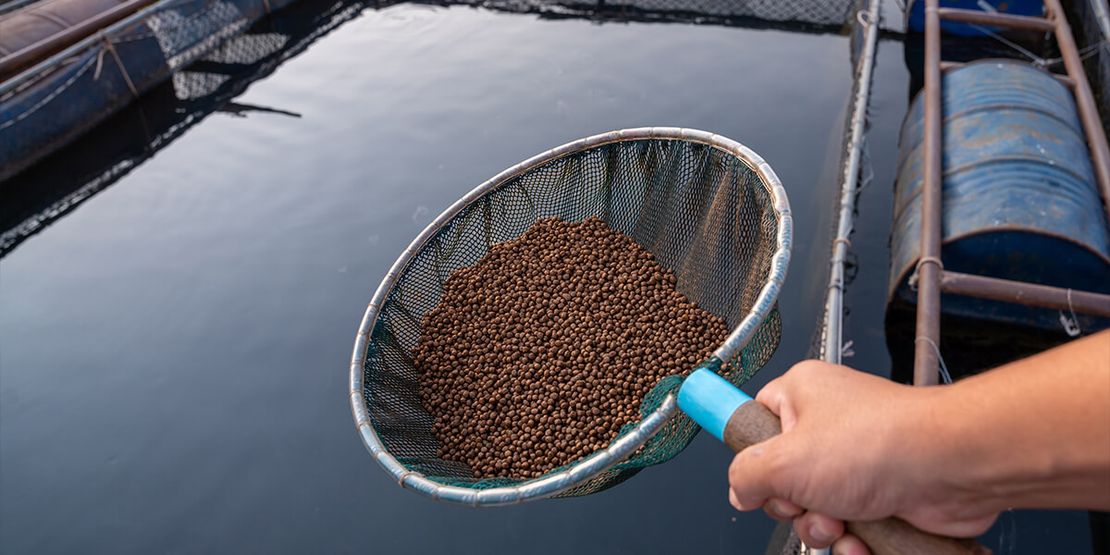
Shrimp, renowned as a delectable seafood choice globally, commands a robust market demand, driving the need for sustainable aquaculture practices. Among the pivotal factors influencing shrimp health and growth, proper feeding stands paramount.
With feed constituting a substantial portion of production costs, selecting the right type of feed becomes imperative for ensuring economic viability and ecological sustainability in shrimp farming.
Understanding Shrimp Feed Options
Shrimp feed encompasses various forms, including pellets, flakes, and powders, each tailored to meet the nutritional requirements of shrimp at different growth stages. These feeds predominantly comprise ingredients such as fish meal, soybean meal, wheat flour, and essential vitamins and minerals. However, the selection of feed type entails considerations of its advantages and drawbacks, as elucidated below:
Commercial Feed
Pros:
- Widely accessible and convenient for farmers
- Formulated to meet shrimp nutritional needs
- Available in versatile forms for ease of administration
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to other feed types
- May contain fillers and preservatives
- Susceptible to concerns regarding ingredient sustainability
Artisanal Feed
Pros:
- Cost-effective alternative, particularly for small-scale farmers
- Utilizes locally sourced ingredients, enhancing control over quality and sustainability
- Offers flexibility in formulation according to specific farm requirements
Cons:
- Time-consuming preparation process
- Potential for variability in nutritional content
- Risk of impurities impacting shrimp health
Natural Feed
Pros:
- Mimics the natural diet of shrimp, promoting health and immunity
- Potential cost-effectiveness, especially with locally sourced organisms
- Enhances environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on processed feeds
Cons:
- Challenges in sourcing required organisms
- Variability in nutritional composition
- Requirement for specialized equipment and storage facilities
Vegetarian Feed
Pros:
- Addresses concerns regarding animal-derived ingredients
- Potential for enhanced sustainability through plant-based formulations
- Suitable for environments where live organisms are unavailable
Cons:
- Potentially higher cost compared to animal-based feeds
- Risk of nutritional inconsistency
- Challenges in sourcing specific plant-based ingredients
Choosing the Right Shrimp Feed
The selection of shrimp feed profoundly impacts shrimp health and growth, underscoring the significance of informed decision-making by farmers. Each feed type presents distinct advantages and limitations, necessitating careful evaluation based on farm-specific requirements, sustainability considerations, and economic viability.
By navigating the diverse array of shrimp feed options, aquaculturists can optimize production outcomes while upholding ecological integrity in the dynamic realm of shrimp farming.
Recommended for you
In Search of Art Tour: Enjoy the Creative Side of Bangkok
Sky, The Bear Traveler
Global Shrimp Industry: Knowing the Key Players and Dynamics
Riley Sinclair (Digital Aqua Bear)