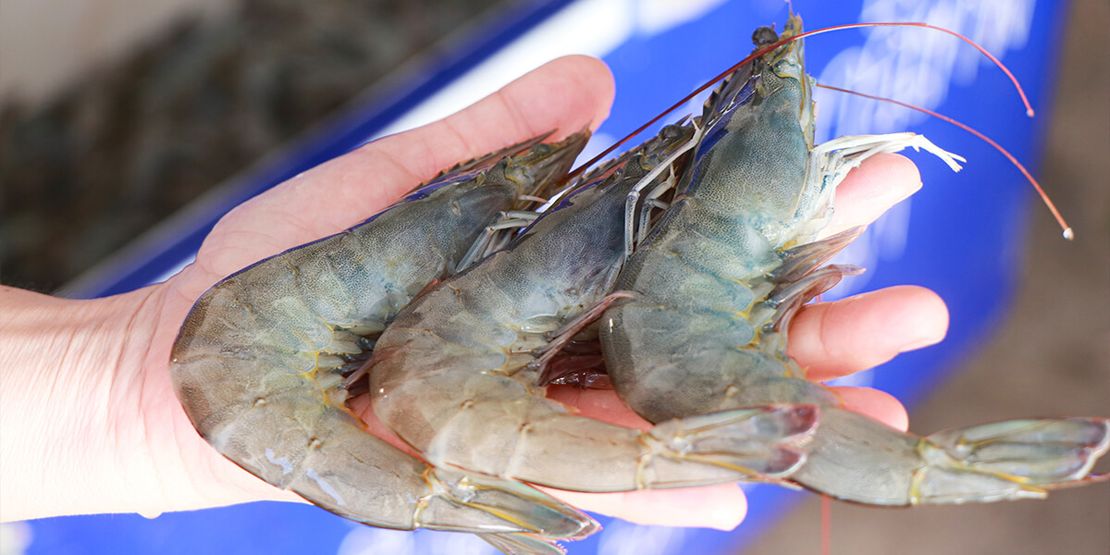
Shrimp Farming with Probiotics: Advantages and Considerations
In the realm of aquaculture, probiotics, live microorganisms offering health benefits to the host when administered in sufficient quantities, have emerged as a promising tool, especially in shrimp farming. The adoption of probiotics in shrimp aquaculture presents a myriad of advantages, including improved water quality, enhanced growth, and bolstered disease resistance, all contributing to elevated survival rates and amplified yields.
However, alongside these benefits, it's vital to acknowledge the nuanced challenges and complexities associated with probiotic use in shrimp farming.
Advantages of Probiotics in Shrimp Farming
Improved Water Quality
Probiotics play a pivotal role in enhancing water quality by metabolizing organic matter and mitigating ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. This remedial action reduces the toxic burden on shrimp, curbing stress-induced susceptibility to diseases.
Enhanced Growth
By bolstering feed conversion efficiency and furnishing vital nutrients, probiotics facilitate accelerated growth rates and bolstered yields. Moreover, the immune-boosting properties of probiotics contribute to the overall vitality and resilience of shrimp populations.
Augmented Disease Resistance
Probiotics exert a competitive inhibition on pathogenic bacteria, impeding their proliferation and reducing the incidence of bacterial infections. Additionally, probiotics stimulate the shrimp's immune system, fortifying their natural defense mechanisms against diseases.
Optimized Gut Health
Colonizing the shrimp gut, probiotics foster a healthy gut flora crucial for efficient digestion, nutrient absorption, and disease resistance. This intestinal equilibrium promotes overall shrimp health and vitality.
Increased Survival Rates
The multifaceted benefits of probiotics culminate in heightened survival rates among shrimp populations, translating to improved yields and profitability for shrimp farmers.
Considerations and Challenges of Probiotics in Shrimp Farming
Strain Selection Dilemma
The diverse array of probiotic strains presents a challenge in selecting the most efficacious one for specific shrimp farming contexts. Moreover, varying effectiveness and suitability for aquaculture further complicate strain selection.
Cost Implications
The adoption of probiotics can entail substantial financial outlay, particularly for small-scale shrimp farms. Expenses encompass not only probiotic procurement but also ancillary costs such as laboratory testing for strain identification.
Complex Application Management
Navigating the intricacies of probiotic application demands meticulous oversight encompassing dosage, timing, and storage protocols. Moreover, specialized equipment and skilled personnel may be requisite, adding layers of complexity and cost to probiotic administration.
Elevating Shrimp Production with Probiotics
The integration of probiotics into shrimp farming holds immense promise for elevating production outcomes and fostering sustainable aquaculture practices. However, it's imperative to weigh the advantages against the considerations and challenges inherent in probiotic utilization.
By discerningly navigating these nuances, shrimp farmers can harness the transformative potential of probiotics while navigating the intricacies of their application to optimize shrimp farming practices for enhanced productivity and ecological stewardship.
Recommended for you
Future of Shrimp Farming: Embracing Indoor Cultivation
Riley Sinclair (Digital Aqua Bear)
Best Countries for Digital Nomads: Finding Remote Work and a New Home
Marc Tubelleja (Curious Bear)
Worst Time to Travel Thailand: A Complete First-Timer's Guide
Dr. Theodore (Professor Bear)
Bangsaray: A Charming Fisherman Village
The Bear Team