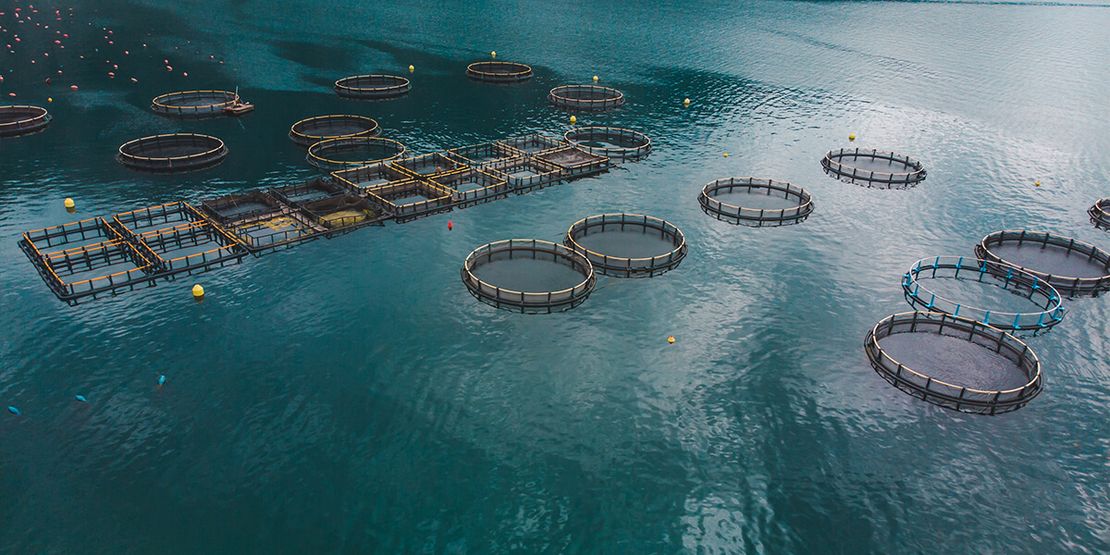
Aquaculture Farming: Essential Terms and Definitions for Beginners (Part 3)
Internet of Things (IoT): A system of connected physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity which enables these objects to collect and exchange data.
Sensor: A device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal that can be read by other devices. Sensors are a key component of IoT devices and are used to collect data such as temperature, pressure, and movement.
Connectivity: The ability of IoT devices to communicate with each other and with other systems, such as the internet, through various communication technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee.
Edge Computing: A technology that enables IoT devices to process data at the source, instead of sending it to a central server for processing. This helps to reduce latency, increase security, and improve overall system performance.
Smart Home: A home that is equipped with IoT devices, such as smart lights, thermostats, security systems, and other connected devices that can be controlled remotely or through a central hub.
Big Data: The vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices, which can be analyzed to gain insights and make better-informed decisions.
Cloud Computing: A computing model that enables data and applications to be stored and processed on remote servers, accessible over the internet. IoT devices often rely on cloud computing for storage and processing of data.
M2M (Machine-to-Machine) Communication: A type of communication between IoT devices, in which the devices can communicate with each other without the need for human intervention.
API (Application Programming Interface): A set of protocols and tools that enable software developers to access and integrate IoT devices into their applications.
Actuator: A device that converts an electrical signal into a physical action. Actuators are used in IoT devices to control physical objects, such as motors, valves, and switches.
Internet of Things (IoT): The interconnectivity of everyday devices, allowing them to communicate and share data over the internet.
Smart Aquaculture: The use of technology in the management and monitoring of aquaculture systems, including the use of IoT devices in shrimp farming.
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN): A network of wireless sensors and devices that are used to monitor and gather data from the shrimp farm environment.
Data Analytics: The use of data to draw insights and make informed decisions. In shrimp farming, data analytics can be used to optimize production and improve overall farm efficiency.
Remote Monitoring: The use of technology to monitor and control the shrimp farm from a remote location.
Automated Feeding System: An IoT-enabled feeding system that uses sensors and data to automate and optimize feeding schedules for the shrimp.
Water Quality Monitoring: The use of IoT devices and sensors to monitor and track water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, and salinity in the shrimp farm.
Inventory Management: The use of technology to track and manage shrimp inventory levels and make informed decisions about stocking levels.
Predictive Maintenance: The use of data and analytics to predict and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving overall farm efficiency.
Real-time Data Collection: The use of IoT devices to collect real-time data from the shrimp farm, allowing for real-time monitoring and decision-making.
Recommended for you
15 Days in Thailand: How Much Money Do I Need?
Dr. Theodore (Professor Bear)
Thailand Golf: Silky Oak Country Club in Rayong
The Bear Team
Thinking Outside the Blog: Guerrilla Marketing Strategies for Bloggers
Virginia Summers (Influencer Bear)
Travel to Eastern Thailand Guide: Everything You Need to Know
Dr. Theodore (Professor Bear)
Travel to Surat Thani Guide: Everything You Need to Know
Dr. Theodore (Professor Bear)