Aquaculture Farming: Essential Terms and Definitions for Beginners (Part 1)
Aquaculture: The farming of aquatic animals and plants for food and other commercial purposes.
Benthic: Refers to the bottom layer of a body of water, where aquatic plants and animals live.
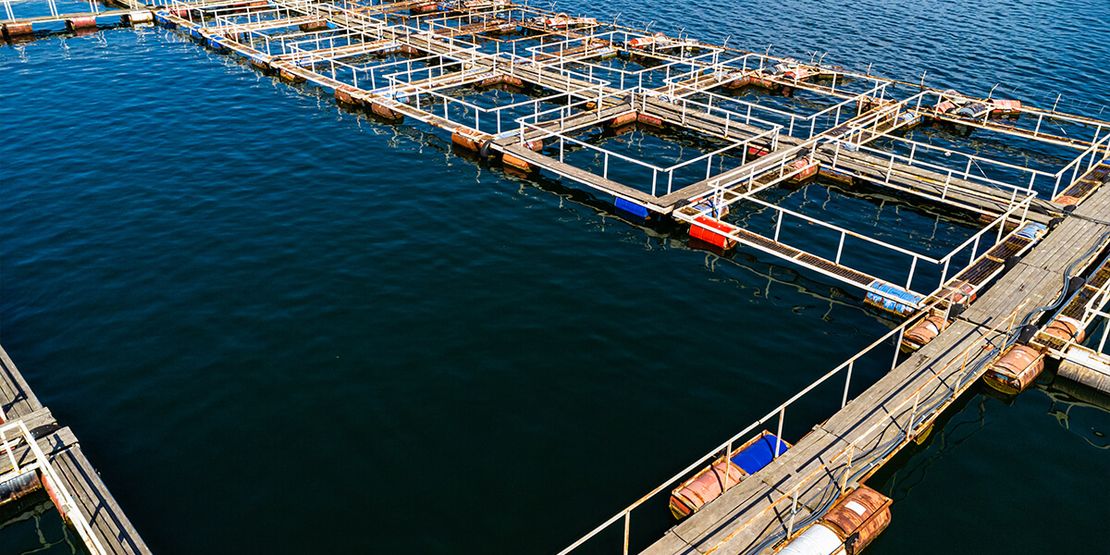
Cage Culture: A method of aquaculture that involves keeping aquatic animals in floating cages, such as for salmon or tilapia.
Copper Sulfate: A chemical commonly used in aquaculture to control parasites and bacteria.
Density Dependent Mortality: A phenomenon in which the death rate of aquatic animals increases as the population density increases.
Eutrophication: The process by which an aquatic ecosystem becomes over-enriched with nutrients, leading to the growth of algae and the depletion of oxygen.
Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR): A measure of the efficiency of food conversion in aquatic animals, calculated as the amount of feed consumed divided by the weight gain of the animal.
Filtrate: The liquid waste produced by an aquaculture system.
Hatchery: A facility where aquatic animals are raised from eggs or larvae for later release into the wild or for aquaculture purposes.
Intensive Culture: A method of aquaculture in which a high density of aquatic animals is kept in a small area, often in tanks or ponds.
Larvae: The early life stage of aquatic animals, before they become juveniles or adults.
Monoculture: A method of aquaculture in which a single species of aquatic animal is raised in large numbers.
Nutrient Loading: The process by which nutrients enter an aquatic ecosystem, often as a result of human activities such as agriculture or aquaculture.
Pond Culture: A method of aquaculture that involves keeping aquatic animals in ponds, often with limited water exchange.
Seedstock: The initial stock of juvenile aquatic animals used in an aquaculture operation.
Water Exchange: The process by which water is moved in and out of an aquaculture system, either to control water quality or to mimic natural conditions.
—
Aquaculture – the cultivation of aquatic organisms in a controlled environment
Algae – single-celled plants that are commonly used as a food source for aquatic animals
Bacteria – microorganisms that play a vital role in maintaining a healthy environment in aquaculture systems
Broodstock – adult fish used for breeding and producing eggs for aquaculture production
Carp – a type of freshwater fish commonly raised in aquaculture
Catfish – a type of freshwater fish that is commonly farmed for its meat
Closed System – a type of aquaculture system in which water is recirculated and not exchanged with the environment
Culture Tank – a container or pool used to cultivate aquatic organisms in an aquaculture system
Cyanobacteria – a type of blue-green algae commonly used as a food source in aquaculture
Dissolved Oxygen – the amount of oxygen present in water, which is necessary for the survival of aquatic animals
Eutrophication – an increase in the nutrient levels in water, which can lead to algal blooms and decreased oxygen levels
Feed – the food given to aquatic animals in an aquaculture system
Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) – the ratio of feed given to the weight gain of aquatic animals
Feedstock – the raw material used to make feed for aquatic animals
Fry – newly hatched fish or shrimp that are used for aquaculture production
Genetics – the study of heredity and variation in aquatic organisms
Hatchery – a facility used to produce and raise aquatic animals for aquaculture production
Larval Stage – the stage of development in which fish or shrimp are in their earliest life stages
Microalgae – tiny algae that are commonly used as a food source for aquatic animals
Net Pens – large underwater enclosures used to farm fish in open water
Nursery – a facility used to raise and care for young aquatic animals before they are transferred to a larger culture tank
Open System – a type of aquaculture system in which water is exchanged with the environment
Oyster – a type of bivalve mollusk that is commonly farmed for its meat
Phototrophic Algae – algae that use light to produce energy through photosynthesis
Pond Culture – a type of aquaculture system in which aquatic animals are raised in man-made ponds
Recirculating System – a type of aquaculture system in which water is recirculated and purified to maintain water quality
RAS (Recirculating Aquaculture System) – a type of aquaculture system in which water is recycled to maintain water quality
Shrimp – a type of crustacean commonly raised in aquaculture
Spawning – the act of producing eggs or sperm by aquatic animals for reproduction
Stocking Density – the number of aquatic animals per unit area in an aquaculture system
Tilapia – a type of freshwater fish commonly raised in aquaculture
Trophic Algae – algae that feed on waste products in aquaculture systems
Aeration – the process of introducing air into water to increase oxygen levels
Algal Bloom – a rapid growth of algae in water, which can have negative impacts on water quality and aquatic life
——-
Aquaculture: The cultivation of aquatic animals and plants, such as fish, mollusks, crustaceans, and seaweed, in controlled environments for food production.
Aquaponics: A type of aquaculture that combines fish farming with hydroponic growing to produce both fish and plants in a symbiotic system.
Fish Feed: Commercial feed pellets specifically formulated for aquaculture species, used to provide them with essential nutrients and energy.
Fry: Newly hatched or juvenile fish used for stocking in aquaculture systems.
Hatchery: A facility used for the artificial production and hatching of fish eggs and the rearing of fry.
Nursery: An area within an aquaculture system used for the rearing and growing of young fish before they are transferred to a grow-out system.
Grow-out: The stage of aquaculture where fish are raised to maturity and reach their target size for harvest.
Harvesting: The process of removing the fish from the aquaculture system for commercial purposes.
Culture System: The type of aquaculture environment used, such as ponds, tanks, cages, or recirculating systems.
Water Quality: The physical, chemical, and biological parameters of the water in an aquaculture system, such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and ammonia levels.
Biofloc Technology: A type of aquaculture system that uses microorganisms to control water quality and provide food for the fish.
Aeration: The process of introducing air into an aquaculture system to increase oxygen levels and maintain water quality.
De-chlorination: The process of removing chlorine from water used in aquaculture systems to prevent harm to the fish.
Filtration: The process of removing solid and dissolved waste products from an aquaculture system to maintain water quality.
Recirculating System: An aquaculture system that recirculates and reuses the water, reducing water usage and environmental impact.
Water Exchange: The process of removing a portion of the water in an aquaculture system and replacing it with fresh water to maintain water quality.
Dissolved Oxygen: The amount of oxygen dissolved in water, which is critical for the health and survival of aquatic animals.
pH: A measure of the acidity or alkalinity of water, which affects the growth and health of fish.
Ammonia: A toxic waste product produced by fish that must be removed from the water to maintain water quality.
Nitrite: A toxic intermediate product produced by bacteria in the nitrogen cycle that must be removed from the water to maintain water quality.
Nitrate: A non-toxic end product of the nitrogen cycle that can be used as a fertilizer for plants in aquaponics systems.
Salinity: The measure of the amount of salt in water, which affects the growth and health of fish and other aquatic species.
Water Temperature: The temperature of the water in an aquaculture system, which affects the growth and metabolism of fish and other aquatic species.
Algal Bloom: The rapid growth of algae in an aquaculture system, which can reduce water quality and harm fish.
Bacteria: Microorganisms that play a critical role in the nitrogen cycle and water quality in aquaculture systems.
pH Buffer: A substance added to water to maintain a stable pH level and prevent sudden
Recommended for you
Global Shrimp Market Dynamics: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities
Riley Sinclair (Digital Aqua Bear)
Hungry Nerd: Appetizing Steak and Pasta in Bangkok
Tle (Hungry Bear)
Pizzeria Da Luigi: An Authentic Italian Restaurant in Bangkok
Tle (Hungry Bear)
Panlee Bakery: A Delightful and Tasty Treat in Bangkok
Tle (Hungry Bear)
Pepper Lunch: A Fast-Steak Restaurant in Bangkok
Tle (Hungry Bear)